What is the GDPR?
The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is a new set of rules designed to offer EU citizens greater control over their personal data. It aims to simplify the regulatory environment for businesses so that both citizens and businesses in the European Union can take full advantage of the digital economy.
What does it mean to be “GDPR compliant”?
According to the terms of the GDPR, organizations must not only ensure that personal data is collected legally and under strict conditions, but those who collect and manage it are required to protect it from abuse and exploitation, as well as to respect the rights of proprietary data – or risk penalties for not doing so.
To whom does the GDPR apply?
The purpose of the new general data protection rules is to impose a uniform law on all EU members, so that each Member State no longer has to write its own laws. In addition to EU members, it is important to note that any company that markets goods or services to EU residents, regardless of their location, is subject to the regulation. As a result, the GDPR will have an impact on data protection requirements globally.
What are personal data pursuant to the GDPR?
The GDPR is designed to protect the personal data of EU citizens and, to this end, regulates the way in which such data is collected, stored, processed and destroyed. The definition of “personal data” is extremely broad: it includes names, addresses and bank details, but also data relating to religion, race, mental or physical characteristics and even IP addresses, web cookies, contacts and mobile device IDs, if they identify an individual.
New Partnership | Arca24 and Lucca
New Partnership | Arca24 and Lucca [...]
Global Staffing Front Office Software Landscape Report 2023 Update
Global Staffing Front Office Softw [...]
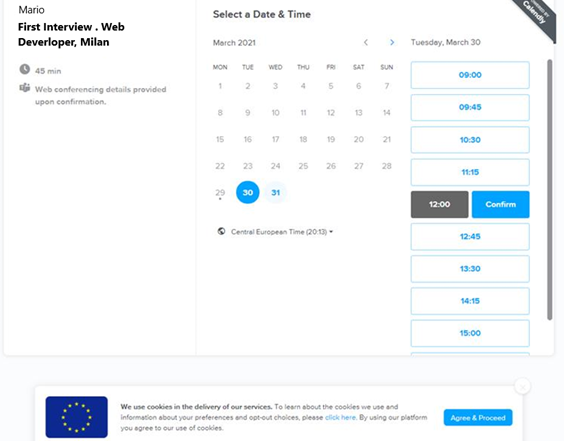
Integration with Calendly
Integration with Calendly Agenda [...]